Satellite decoder block¶
The Satellite decoder block brings most of the functionality of the
gr_satellites command line tool in the form of a GNU Radio block. This
allows the experienced user to leverage the functionality of the satellite
decoders in their own designs or to achieve a greater degree of customization
than what is possible with the command line tool.
The input of the Satellite decoder block is a stream of samples, which can be
either real or complex, for IQ input (see Real or IQ input). The output
of the block is PDUs with the decoded frames. The figure below shows a very
basic use of the Satellite decoder block, where the input is taken from a WAV
recording using the Wav File Source block and the output is printed using the
Message Debug block. This example can be found in gr-satellites in
examples/satellite_decoder/satellite_decoder.grc.
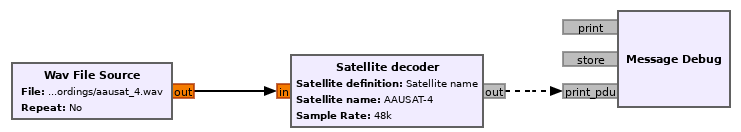
Usage of Satellite decoder in a flowgraph
The figure below shows the options for the Satellite decoder block. It is
possible to specify the satellite to use in the same ways as for the
gr_satellites command line tool (see Specifying the satellite). The
method to specify the satellite is chosen in the “Satellite definition”
dropdown menu. The sample rate needs to be entered in the “Sample Rate” field,
and the “IQ input” field selects real or IQ input.
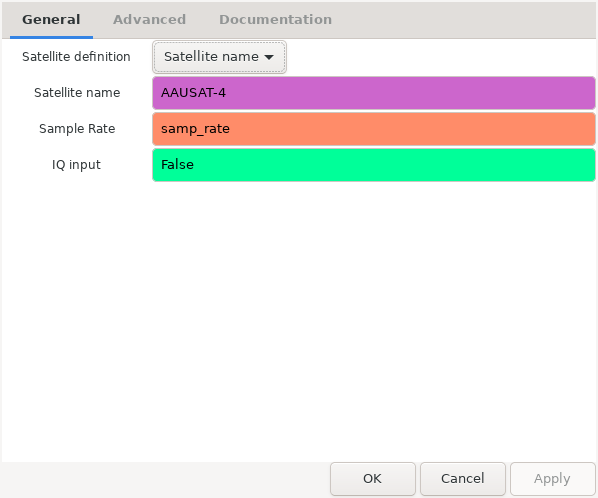
Options of Satellite decoder
Here are a few ideas of how the Satellite decoder block can be employed by users to build custom decoders which are not possible with the command line tool.
On the input side, it is possible to use all the standard GNU Radio blocks to support a large number of SDR hardware and recording formats. The different channeliser and filter blocks (especially “Frequency Xlating FIR Filter”) can be used to adapt the sample rate and bandwidth of the signal into something useful for the satellite decoder. For example, a wideband SDR might be used to receive the signal of different satellites, performing Doppler correction with gr-gpredict-doppler. The signals of these satellites might be channelised with a “Frequency Xlating FIR Filter” blocks and fed into independent Satellite decoder blocks.
On the output side, it is possible to treat the received PDUs freely. This allows classifying and storing them in different ways. Upper layer complex protocols might be completely handled inside the GNU Radio flowgraph, provided there is a suitable implementation of these protocols. Additionally, it is possible to interface the decoder to external tools with default GNU Radio blocks, by using TCP sockets or ZeroMQ.